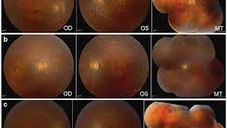
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
DHDDS-related retinitis pigmentosa (RP) 59 is a rare genetic disorder that causes the retina to degenerate. DHDDS stands for dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase, a gene that encodes a subunit of the enzyme cis-prenyltransferase (CPT). CPT is required for the synthesis of dolichol, which is a protein glycosylation cofactor. RP59 is caused by a recessive mutation in the DHDDS gene, which changes the 42nd amino acid of the DHDDS enzyme from lysine to glutamic acid. This change is known as a K42E point mutation. RP59 causes the rod cells in the retina to break down first, which typically leads to loss of night vision in childhood. As the disease progresses, blind spots develop in peripheral vision, which eventually merge to create tunnel vision. Finally, central vision gradually declines. RP59 affects one in 100 Ashkenazi Jewish people and one in 2,009 people worldwide.
At present, there is no cure for RP, but medications can help treat complications. A medical professional can diagnose and manage RP to improve symptoms.